A herniated disc with belly
A herniated disc is a common condition that affects the spine. It occurs when the soft, jelly-like center of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the outer layer, causing pain and discomfort. While herniated discs can occur in any part of the spine, they are most common in the lower back.
One of the symptoms of a herniated disc in the lower back is pain in the belly muscles. This pain can be caused by pressure on the nerves that run through the spine and into the abdominal muscles. The pain may be sharp or dull and can be felt in the lower back, buttocks, and legs.
In addition to pain, a herniated disc can also cause weakness and numbness in the affected area. This can make it difficult to perform everyday tasks such as walking, standing, and sitting. In severe cases, a herniated disc can even cause loss of bladder or bowel control.
Treatment for a herniated disc with belly muscle pain typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and pain medication. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove the herniated disc and relieve pressure on the nerves.
Preventing a herniated disc with belly muscle pain involves maintaining good posture, exercising regularly, and avoiding activities that put excessive strain on the back. It is also important to maintain a healthy weight and avoid smoking, as these factors can increase the risk of developing a herniated disc.
In conclusion, a herniated disc with belly muscle pain can be a painful and debilitating condition. However, with proper treatment and prevention measures, it is possible to manage the symptoms and prevent further damage to the spine. If you are experiencing symptoms of a herniated disc, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the best course of treatment.A herniated disc with belly muscles is a health condition that can cause severe pain and discomfort for people. This condition affects the spinal discs that are located between the vertebrae of the spine. The spinal column is made up of a series of bones called the vertebrae. These bones join together to form a long, narrow, and flexible tube that runs down the center of the back. This tube is called the spinal canal, and it contains the spinal cord and nerve roots.
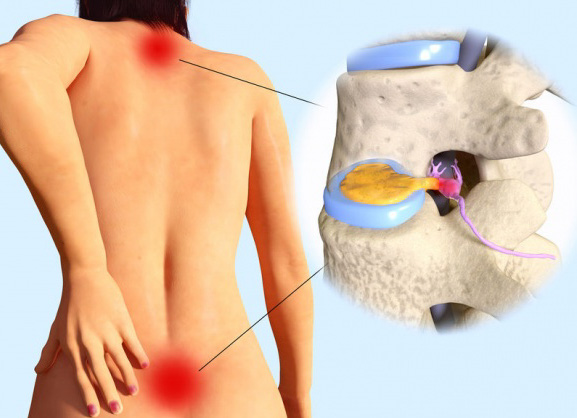
The spinal discs are tough, rubbery cushions that sit between each vertebra, acting as shock absorbers and allowing the spine to maintain flexibility. These discs are made up of a tough outer layer called the annulus fibrosus and a soft, jelly-like inner layer called the nucleus pulposus. A herniated or slipped disc occurs when the annulus fibrosus tears or ruptures, allowing the nucleus pulposus to leak out and press against the spinal cord or nerves.
While a herniated disc can occur in any part of the spine, it is most common in the lower back or lumbar region, where the discs experience the greatest amount of pressure and stress. A herniated disc can cause a range of symptoms depending on the severity and location of the herniation. Common symptoms include pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the affected area.
In some cases, a herniated disc can also affect the muscles of the abdomen, including the belly muscles. The spine and the abdominal muscles are closely connected, and any issue in one area can affect the other. When a herniated disc occurs in the lumbar region of the spine, it can compress the nerve roots that supply sensation and muscle control to the abdominal muscles.
The deep muscles of the abdomen are responsible for stabilizing the spine and maintaining proper posture. When these muscles are compromised, it can lead to weakness, instability, and pain in the lower back. The effects of a herniated disc on the abdominal muscles are often subtle but can include difficulty with sit-ups or other exercises that require using the core muscles.
Treatment for a herniated disc with belly muscle involvement may include a combination of rest, physical therapy, medications, and, in severe cases, surgery. Rest is essential for allowing the damaged disc to heal and limiting further damage. Physical therapy can help to strengthen the muscles around the spine, improve flexibility and mobility, and reduce pain and discomfort.
Medications can help to manage pain and inflammation associated with herniated, however, I recommend you to have 6 packs built that could help you to resist against disc herniation which is one of the way to balance muscles surrounding the middle body, either one is assumed to be weaken between front muscle and back when disc has been herniated at young age, but those who work with sitting all day could have their front belly muscle been weaken from not enough exercise daily, then the spin can lose balance causing disc herniation by high rate from my experience.




Comments
Post a Comment